| Reflecting fuel performance experience gained over the past decade, the handbook provides a comprehensive reference for predicting fuel failures through monitoring, trending and interpreting activity release data.
EPRI has updated the Fuel Reliability Monitoring and Failure Evaluation Handbook (EPRI Report 1019107) based on operating and fuel failure experience collected since the last update in 2003. The handbook documents the essential elements of an effective fuel integrity monitoring program, including reviewing fuel performance data, trending fission product nuclides, estimating the number and exposure of leaking fuel rods, and identifying failure mechanisms.
The handbook provides information on boiling water reactor (BWR) and pressurized water reactor (PWR) fuel release activity monitoring techniques, and also presents an in-depth method for assessing fuel failures and secondary degradation. Three sections of photographs document common fuel failure mechanisms as a utility reference in root cause analyses.
 |
|
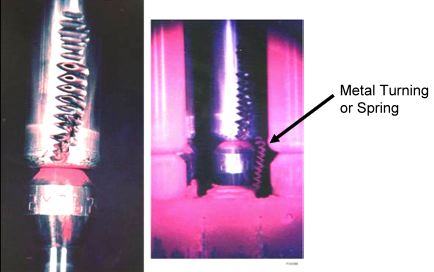
| Debris fretting marks caused by a metal turning or spring |
|
The update incorporates plant experience and technical knowledge gained from fuel failures and related subjects over the last decade. Revisions include recommendations for techniques to monitor tight defects in PWRs, better prediction of the burnup of a failed rod, assessment of changes in activity release characteristics due to noble metal application in BWRs, and a methodology for calculating dose equivalent Xe-133 for PWRs. New chapters on BWR power suppression testing and a sample failed fuel action plan provide useful reference information for managing fuel failure events and improving fuel reliability. The handbook also updates industry knowledge with respect to fuel failure root causes and mitigation measures for both BWRs and PWRs.
As part of the industry’s zero fuel defect initiative, the Institute of Nuclear Power Operations (INPO) has referenced the techniques in the handbook during reviews of plant fuel reliability monitoring programs. Specifically, the methodologies for determining the presence of fuel failure and estimating the number of failed rods from activity release data as described in the handbook have been adopted.
The Fuel Reliability Monitoring and Failure Evaluation Handbook (Revision 2) is now available. For more information, contact Bo Cheng at 650.855.2442 or bcheng@epri.com.
|